Option Delta – One of the four greeks. Today, I’ll talk about Delta, which helps us understand how our option positions are expected to change, based on changes in specific environmental factors such as changes in underlying security over time and changes in implied volatility.
I’ll focus on Delta. Understanding it will improve your financial education for investors of all levels. there are several definitions for understanding Delta.
It represents the amount the options price will change for a $1 move in the stock, or the second definition is the probability for the option to expire in the money.
While an option delta indicates how much the option price will change if the price changes by $1.
I know this is overwhelming,
So let’s go through a series of examples, and by the end of this post, you’ll know very well what Delta represents.
As I’ll go through numerous examples to demonstrate each of the concepts I’ll discuss.
Table of Content
- How Delta is Calculated
- Calculation Delta Formula
- Deltas for Call Options
- Deltas for Put Options
- Google Stock Example
- Pons and Cons
- What is delta risk?
- Bottom Line
How Delta is Calculated
let’s start with Delta: Where do these Greeks come from? The Greeks are the results of a pricing model that most of you’ve probably heard of – the Black- Scholes pricing model is certainly the best-known of them all.
let’s see how it works, consider different options with different delta values expected,
For example, let’s consider a
call option = $3
Delta = 0.6
Strike Price = $140
If the price increases by $1, meaning the underlying asset’s price now is $141.
the option price would pick up 60 cents, the call option is expected to be positive delta $3.60,
and if the underlying security decreases by $1, the option price will be less by 60 cents. the call option is expected to be $2.40.
So, the delta shows us how sensitive options prices are to changes in the underlying security.
with the put option, the logic is the same, except that with the put option we’ll have a negative delta.

Another scenario is if we have a put option
Put = $3
Delta = – 0.40
Strike Price = $140
Put option benefit from falling stock prices but the concept is exactly the same
then the delta of this put option is expected to change to a negative delta of -0.40.
when the underlying security increases by $1, that put option going to lose Delta value of 40 it’s going to lose about 40 cents.
meaning the option will be trading at a positive delta of $2.60.
so in this scenario, if the stock price Falls $1 right now to 139, that 140 puts are going to pick up about 40 cents.
so now it trades for $3.40,
Remember that call options increase their prices as the underlying security rises put options increase as it falls.
Calculation Delta Formula
Option Expiration
Another important aspect of options pricing when you are at expiration all options are worth either 0 if they’re out of the money or at the money.
Or they are worth their intrinsic value and there’s no in-between. it’s either 0 or intrinsic at expiration.
options are derivatives, which means that the option price is derived from the underlying stock’s price.
delta for calls can range from 0 to 1
delta for puts can range from 0 to -1
Deltas for Call Options
In case you’re super bullish on a stock like XYZ, you can buy a call option instead of the stock itself.
So if the delta of a call option is 0.30, or delta 30, that means the call option moves $30 for every dollar the underlying stock goes up.
If the delta of a call option is 0.70 or delta 70, it means that the call option moves $70 dollars for every dollar the underlying stock rises.
Remember that high returns like this also come with high risk, because you can increase your profits exponentially by buying calls, but you can also lose them exponentially if the stock price goes the other way.
Deltas for Put Options
If the price of the underlying share falls, the value of the put rises, and if the price of the underlying share rises, the value of the put falls.
Realize that you can make money when the stock price goes down!
you don’t always have to make the stock go up to make money, and that’s the beauty of options trading.
Google Stock Example
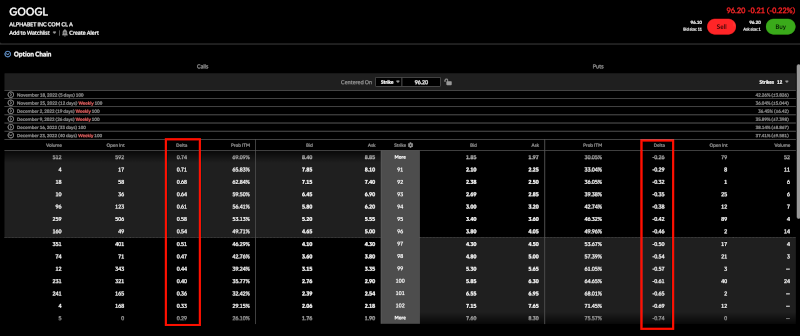
Call Option delta
let’s take a look at some real-life examples. Look at one of my favorite stocks, Google, ticker symbol Googl.
You can see that Google is at $96 right now. I’m going to look at the option chain. Expiration December 23.
let’s take a look at some of these deltas. On the left side are all the call options and on the right side are all the put options.
you can see that the higher you go or the deeper you’re in the money, the higher the delta on the call options.
however, when you go out of the money, you can see that the delta starts to shrink.
Put
You can see that it’s a bit reversed on the put side.
The further you go into the money, the higher the absolute value of the delta. You can also see that the further out of the money you go, the lower the absolute value of the delta.
The further in the money you go or the higher the delta is, the higher the price will be.
and the same is true on the Put side, the further in the money you go or the higher the delta is.
Pons and Cons
The delta is the rate of change of an option price for a $1 increase or decrease in the underlying asset price.
It’s important to know that
having positive deltas when I want the underlying to go up ( buy calls or sell puts).
having negative deltas when I want the underlying to go down ( sell calls and buy puts).
I want the underlying to go up, the deltas will be positive, if I want the underlying to go down, they’ll be negative.
Another point is that you’ve to mark your directional risk. The more deltas you’ve, the greater your directional risk.
If the underlined value is in your favor, that’s a good thing in terms of profitability, but if it goes against you, you lose more money.
And last but not least, we can hedge our positions with delta. if you imagine that a stock is 1 delta, regardless of how many shares you’ve, you can hedge that by buying/selling options to offset the directional risk.
What is delta risk?
Many people lose a lot of money just by gambling options.
When you are options trading, you also need to understand other variables like theta decay and implied volatility.
As a trader, you’re a risk manager, and one of the reasons we love options so much is that they give us the ability to manage risks better than any other instrument in the world.
Risk management actually begins with delta so let’s find out why…
Delta means the slope of the risk profile.
and that’s what poses the greatest risk. Have you ever had a trade go against you?
it’s because of the delta. The stock just moved a lot or moved pretty fast and aggressively and took the option out of the money.
You can see that the more deltas you put into a position, the more you can earn if it goes in your favor,
but the more you can lose if it goes against you.
Focus on the downside of the slop first.
What the potential losses are, and it’s the delta losses that are the biggest in most cases.
Now you know a little more about delta risks.
Bottom Line
Like the ancient gods, the Greeks watch over certain areas – including price, time, and implied volatility.
The Greeks are an important part of options trading because they tell you how changes in certain factors can affect the option’s price.
The Delta: Like Zeus, the Delta is the ruler over all other option Greeks, as it often has the greatest impact on the value of an option.
The Domain of the delta is the price.
It indicates how much the option premium can change if the underlying price changes by $1.00.
Delta has another important function. Some traders use it to estimate the probability that an option will expire in the money.
For example, an option with a delta of 0.50 can also be interpreted as having a 50% chance of expiring in the money.
Expiration, The lower the delta, the less likely the option is to expire in the money.
An important note about the delta is that it doesn’t change constantly.
It grows as an option goes further in-the-money, and shrinks as it goes further out of the money.
